Gorakhpur deaths: NHRC calls it gross callousness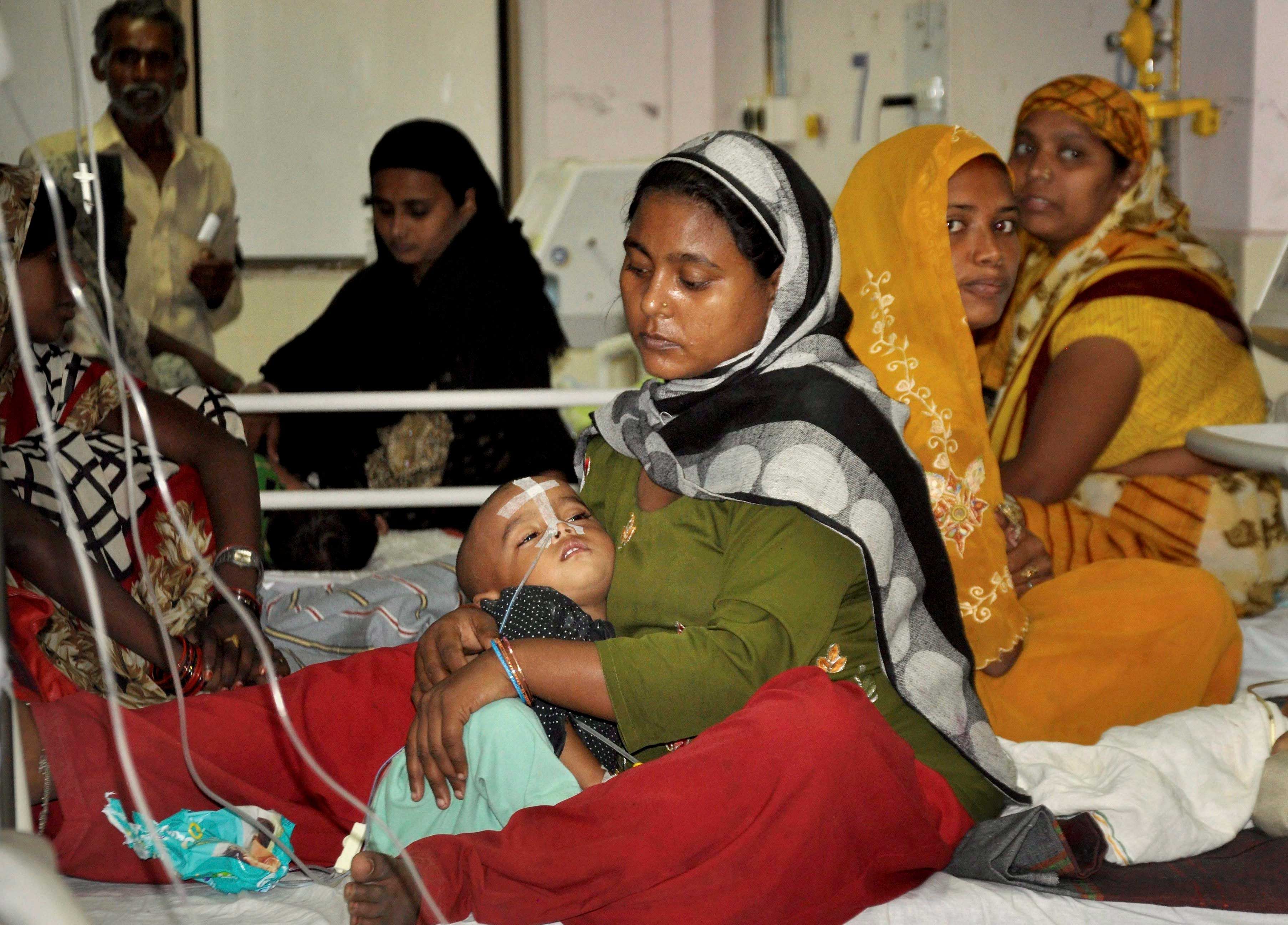
Last Updated IST

The NHRC took suo motu cognizance of the death of over 60 children in BRD Medical College in Gorakhpur came following media reported negligence on the part of the administration in the supply of liquid oxygen at the hospital. PTI file photo
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) on Monday sought a report from Uttar Pradesh government on the death of children in Gorakhpur, saying it indicated "gross callousness" on the part of the hospital and the state administration.
It said “nothing has improved” despite the assurance the administration gave to the NHRC just days before on improving the situation.
The NHRC took suo motu cognizance of the death of over 60 children in BRD Medical College in Gorakhpur came following media reported negligence on the part of the administration in the supply of liquid oxygen at the hospital.
The state Chief Secretary has been asked to submit a detailed report within four weeks on the deaths and steps taken for relief and rehabilitation of the affected families. The NHRC also wants to know what action has been taken against the guilty officers.
The "reported deaths, in such a large number in a government run hospital, amount to serious violation of Right to Life and Health of the innocent victims. This indicates towards gross callousness on part of the hospital administration and the Medical Education and Health Department of the Government of Uttar Pradesh," the NHRC said in a statement.
Earlier also, it said, it has come across several instances of deaths in the hospitals due to Japanese Encephalitis.
The NHRC said the issue of deaths due to Japanese Encephalitis was discussed with the Chief Secretary and senior officers during its recently concluded Open Hearing and Camp Sitting at Lucknow between August 9 and 11. "However, in spite of assurance given by the state administration, the situation has not improved," the statement said.
Quoting media reports in both English and Hindi media, it said the private firm contracted to supply liquid oxygen to the BRD Medical College stopped the supplies, as it was not paid the outstanding dues of almost Rs 70 lakh. The "result was tragic deaths" of about 60 children admitted in the neonatal and encephalitis wards of the hospital.
A magisterial inquiry has been ordered by the administration to ascertain the cause of death. In the last three decades, Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) have claimed over 50,000 lives in the eastern Uttar Pradesh, mostly in the Gorakhpur district.
According to media reports, 124 deaths were reported in the hospital this year till August 8 while 641 children died last year and 491 in 2015.
It said “nothing has improved” despite the assurance the administration gave to the NHRC just days before on improving the situation.
The NHRC took suo motu cognizance of the death of over 60 children in BRD Medical College in Gorakhpur came following media reported negligence on the part of the administration in the supply of liquid oxygen at the hospital.
The state Chief Secretary has been asked to submit a detailed report within four weeks on the deaths and steps taken for relief and rehabilitation of the affected families. The NHRC also wants to know what action has been taken against the guilty officers.
The "reported deaths, in such a large number in a government run hospital, amount to serious violation of Right to Life and Health of the innocent victims. This indicates towards gross callousness on part of the hospital administration and the Medical Education and Health Department of the Government of Uttar Pradesh," the NHRC said in a statement.
Earlier also, it said, it has come across several instances of deaths in the hospitals due to Japanese Encephalitis.
The NHRC said the issue of deaths due to Japanese Encephalitis was discussed with the Chief Secretary and senior officers during its recently concluded Open Hearing and Camp Sitting at Lucknow between August 9 and 11. "However, in spite of assurance given by the state administration, the situation has not improved," the statement said.
Quoting media reports in both English and Hindi media, it said the private firm contracted to supply liquid oxygen to the BRD Medical College stopped the supplies, as it was not paid the outstanding dues of almost Rs 70 lakh. The "result was tragic deaths" of about 60 children admitted in the neonatal and encephalitis wards of the hospital.
A magisterial inquiry has been ordered by the administration to ascertain the cause of death. In the last three decades, Japanese Encephalitis (JE) and Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) have claimed over 50,000 lives in the eastern Uttar Pradesh, mostly in the Gorakhpur district.
According to media reports, 124 deaths were reported in the hospital this year till August 8 while 641 children died last year and 491 in 2015.
