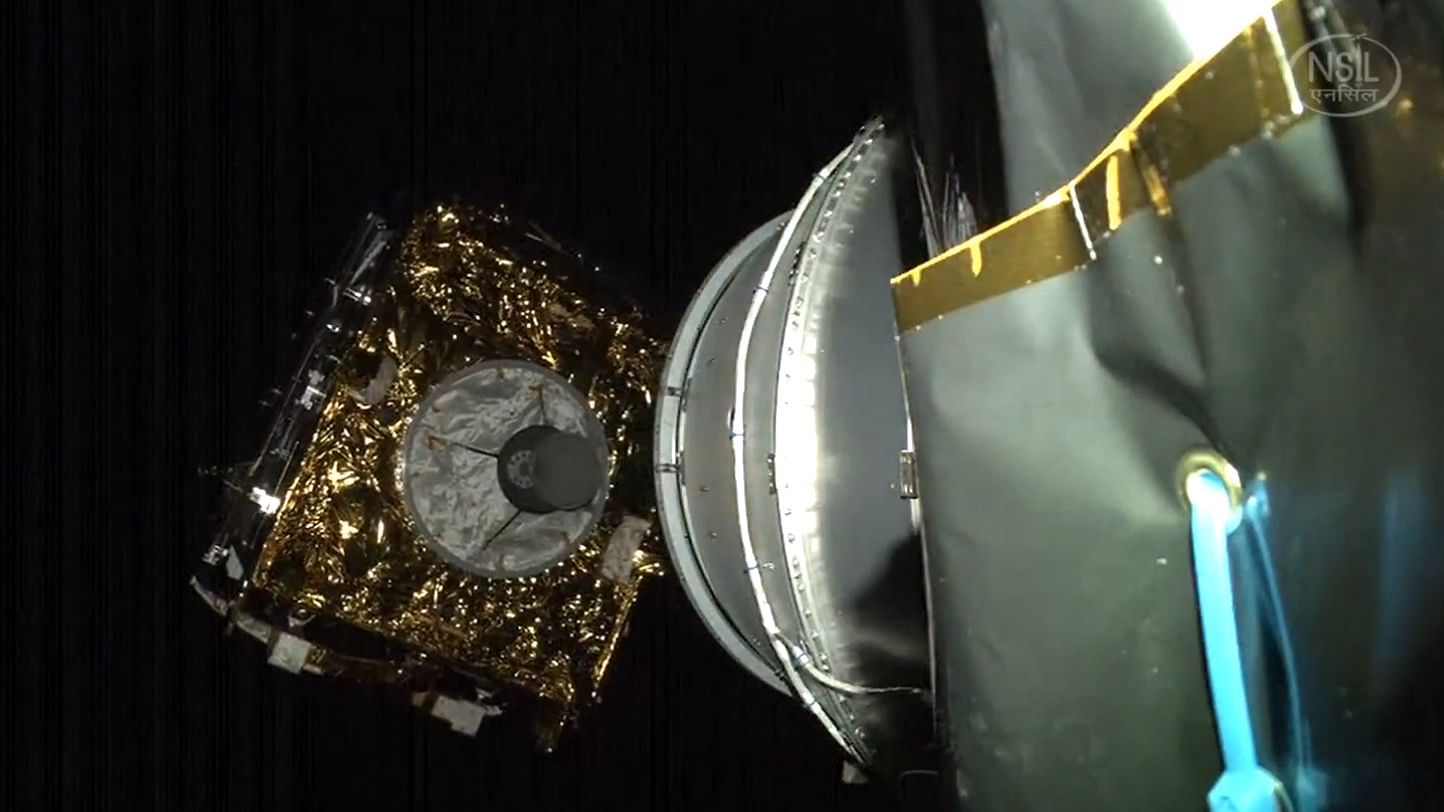
GSAT-N2 deployment
Credit: X/@SpaceX
Bengaluru: The country's latest communication satellite, GSAT-N2 was successfully launched by billionaire Elon Musk-founded SpaceX from Cape Canaveral in the US, ISRO's commercial arm NSIL has said.
The communication satellite will enhance broadband services and in-flight connectivity across the Indian region, NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) said.
As the satellite was heavier than ISRO's current launch capabilities, it had to opt for a foreign launch vehicle, top space scientists and former chiefs of the country's space agency said.
Speaking to PTI, former ISRO chairperson K Sivan said, "the satellite was a heavier one beyond the capability of ISRO launch vehicles, that's why it has gone outside." The 4,700kg GSAT-N2 High-throughput (HTS) satellite onboard a Falcon 9 rocket was injected into the desired orbit. "NSIL's GSAT-N2 High-throughput (HTS) Communication satellite successfully launched from Cape Canaveral, USA on 19th November 2024."
"GSAT-N2 weighing 4700 kg has been injected into the desired Geo-synchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) and ISRO's Master Control Facility (MCF) has taken control of the satellite. Preliminary data indicates satellite in good health," NSIL said in a post on 'X.'
The second Demand Driven satellite of NSIL, GSAT-N2 is a Ka-band High throughput communication satellite that will enhance broadband services and in-flight connectivity across the Indian region, NSIL said. GSAT-24 was NSIL's first demand driven satellite and launched from Kourou, French Guiana on June 23, 2022.
"This satellite (GSAT-N2) featuring multiple spot beams and wideband Ka x Ka transponders, aims to support a large subscriber base with small user terminals, boosting system throughput through its multi-beam architecture which allows frequency reuse," NSIL said.
The satellite has a mission life of 14 years and is equipped with 32 user beams, comprising eight narrow spot beams over the Northeast region and 24 wide spot beams over the rest of India.
"These 32 beams will be supported by hub stations located within mainland India," NSIL said. The payload consists of three parabolic 2.5-meter deployable reflectors with multiple feeds generating 32 spot beams over the Indian region using a single feed per beam configuration. The GSAT-N2 spacecraft structure is based on the standard Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP)-based I4K bus.
ISRO, which has of late been launching foreign satellites from its spaceport in Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh, had to opt for SpaceX to launch its latest 4.7 tonne satellite since it lacked the facilities for the heavier payload. According to Sivan, ISRO has a capacity of four tonne whereas the GSAT-N2 weighs 4.7 tonne. "There are plans to increase the capabilities of ISRO and the activities are going on," the former ISRO chief said.
He explained that the GSAT-N2 will provide high-band communication services to India, making it reach even the remotest parts of the country. Former ISRO chief G Madhavan Nair told PTI that India opted for a bigger launch vehicle to carry 4.7 tonne satellite because it did not have such a facility here. "ISRO has plans to double its next generation vehicles capacity, but we can't wait until then, so they opted for SpaceX," he said.