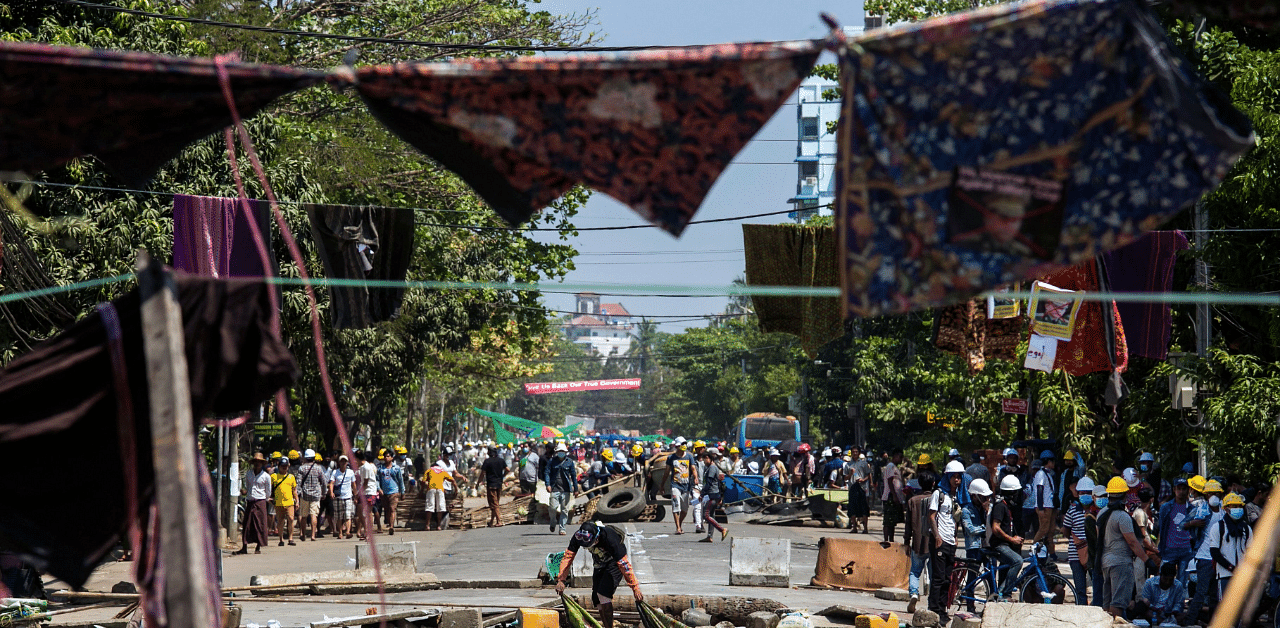
As women take a frontline role in anti-coup protests in Myanmar, some have found an inventive way of defying military rule - hanging traditional sarongs, underwear and even sanitary pads in the streets to spook superstitious policemen and soldiers.
The movement, dubbed the "Sarong Revolution" by feminists, plays on a belief that deems it bad luck for men to walk beneath women's clothing, and highlights women's fears that the Feb. 1 coup could roll back hard-won gains on gender equality.
"The htamein (sarong) has become our tool at the protests," said Naw Esther Chit, 28, an ethnic Karen activist who has been tear-gassed at several protests against the ouster of Aung San Suu Kyi's elected government.
"Women's items are used because of the belief that men would be seen weaker if they walk beneath the htamein ... police have to take them down and it gives us time to run for safety," she told the Thomson Reuters Foundation by phone.
The unusual movement's nickname echoes the "Saffron Revolution" - pro-democracy protests led by Buddhist monks in 2007 that helped pave the way towards democratic reforms.
During weeks of unrest since the coup, police have fired tear gas, rubber bullets and stun grenades to disperse protesters, and women have not been spared.
One of the most striking images from the protests was a young woman wearing a T-shirt that read "Everything will be ok" before she was shot dead, one of about 70 people who have been reported killed since the demonstrations began.
The junta has said it is acting with utmost restraint in handling what it describes as demonstrations by "riotous protesters" whom it accuses of attacking police and harming national security and stability.
'Fight for democracy'
It is not the first time that women have played a prominent role in pro-democracy protests in Myanmar, which started a decade of democratic reforms in 2011 after nearly half a century of rule by successive military juntas.
"Women have been a backbone in Myanmar's fight for democracy, not just in 1988 but they have been fighting since the British colonial rule," said Tanyalak Thongyoojaroen, an associate with Fortify Rights, a Bangkok-based regional human rights group.
Women including university students turned out in force in a 1988 uprising against the military - the protests that first brought Nobel laureate Suu Kyi to prominence.
Suu Kyi's party won a 2015 election and established the country's first civilian government in five decades. She was re-elected in November before the military seized power last month, saying the poll was marred by fraud - an assertion rejected by the electoral commission.
In the latest turmoil, women including nurses and teachers have taken to the streets and social media to protest, with some worried that women's rights could be rolled back by the male-dominated junta, based on its previous record.
"What's different this time is that women are not only fighting for democracy and condemning the coup but at the same time they're also calling for an end to the patriarchal military and fighting for gender equality," Thongyoojaroen said.
Despite their visible presence in anti-coup demonstrations, women in Myanmar - except for Suu Kyi - are largely absent from leadership roles in the country, where gender inequalities are widespread and domestic violence is not outlawed.
It is ranked 114 out of 153 countries on the World Economic Forum's 2020 Global Gender Gap Index, after scoring poorly on women's political empowerment and economic participation.
Anger over such entrenched inequality spurred Su Su, a 22-year-old filmmaker, to take to the streets.
She has been tear-gassed on numerous occasions and her hand was struck by a police baton, but she said she was determined to continue defying the military junta and fighting for women's rights.
"I joined the protests because of the injustices," she said. "I want equality for all."